4 advantages (and 1 disadvantage) of desiccant dehumidifiers
Feb 20, 2025High humidity can be unpleasant. If you're choosing a dehumidifier, this brief overview of the advantages and disadvantages...
The heat wave that has been decimating western Europe for a few days has already arrived in the Czech Republic. The weather here will be a bit milder than, for example, in England or Spain, even temperatures around 36 °C are no honey and will surely torment a lot of us. In recent years, it has also been shown that high temperatures negatively affect the quality of the air around us. How does this happen and what are the risks for us?
Heat waves threaten our health, as well as impurities in the air. Then, when hot weather arrives, warnings about the dangers of heat and air pollution often go hand in hand. Why is this so and what are the mechanisms behind it? Warm air can increase air pollution levels in three different ways:
Heat means more energy use by air conditioners in buildings and cars, and this extra energy use causes more air pollution. In terms of temperature reduction, air conditioning is the most effective solution. But not everyone wants or can have air conditioning at home. A great alternative is the Airbi ZEPHYR column fan with two different blowing directions at once.
Climate change with longer warm seasons may also cause greater production of plant allergens, i.e. pollen.
Also, the side effects of warm weather can significantly increase air pollution. For example, the fires that can be seen every year in southern Moravia or on the Balkan coasts produce a large amount of dirt. Thanks to windy weather, these pollutant particles can reach densely populated areas and harm their inhabitants.
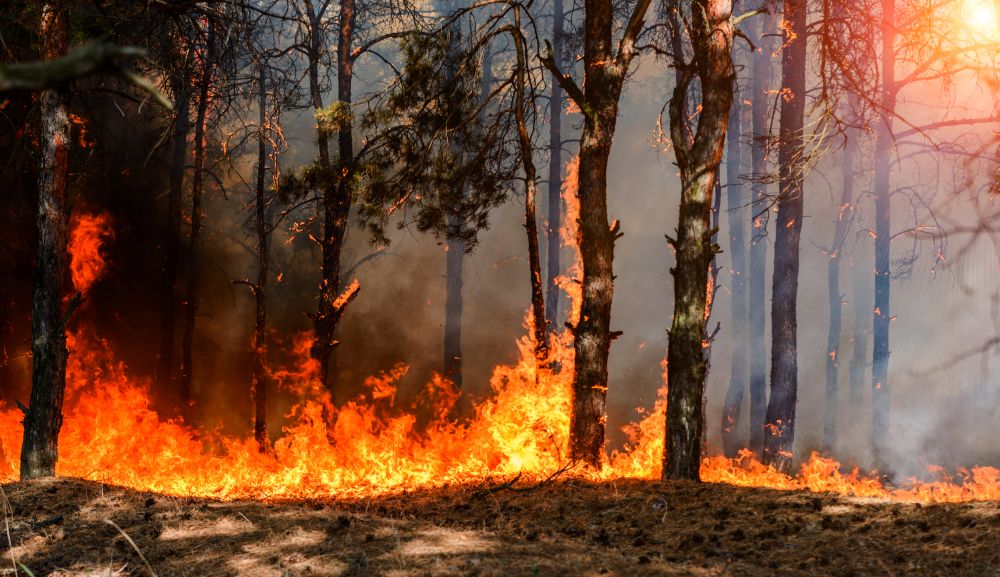

Wild fires devastate the landscape and the environment
Solar radiation and high temperature trigger chemical reactions between primary air pollutants (e.g. nitrogen oxides from car exhausts) and oxygen. The subsequent chemical reaction creates a dangerous oxidant for our respiratory system - ozone. The warmer the day and the more intense the sun, the more ozone is produced. The result is a deterioration in the condition of asthmatics, but also breathing problems in otherwise healthy people.
Heat and sun also transform primary particles into secondary, smaller particles that can be more toxic. These secondary particles, which are photochemically produced by sunlight, are of fundamental importance. They are ubiquitous and can make up to 90 percent (by number) of total particles. Secondary particles are about one-thousandth of a millimeter or even smaller in size. When inhaled, they can get deep into the respiratory tract and even enter the blood and spread throughout the body.
"Ultrafine particles account for 80% of the particles in urban air," says Francelyne Marano, professor of biology at the University of Paris. "But we don't have any technology to measure them accurately. That's why there is currently no regulation for ultrafine particles."
A team of researchers from the University of Bern, Switzerland, recently demonstrated that secondary particles from the combustion of fuels in engines directly harm the respiratory tract and at the same time, thanks to their physical and chemical properties, weaken our defenses. As a result, lung tissue can be damaged much more easily, and pathogens (viruses, bacteria) can more easily enter the lungs. The most at-risk group are asthmatics and people suffering from other lung diseases.
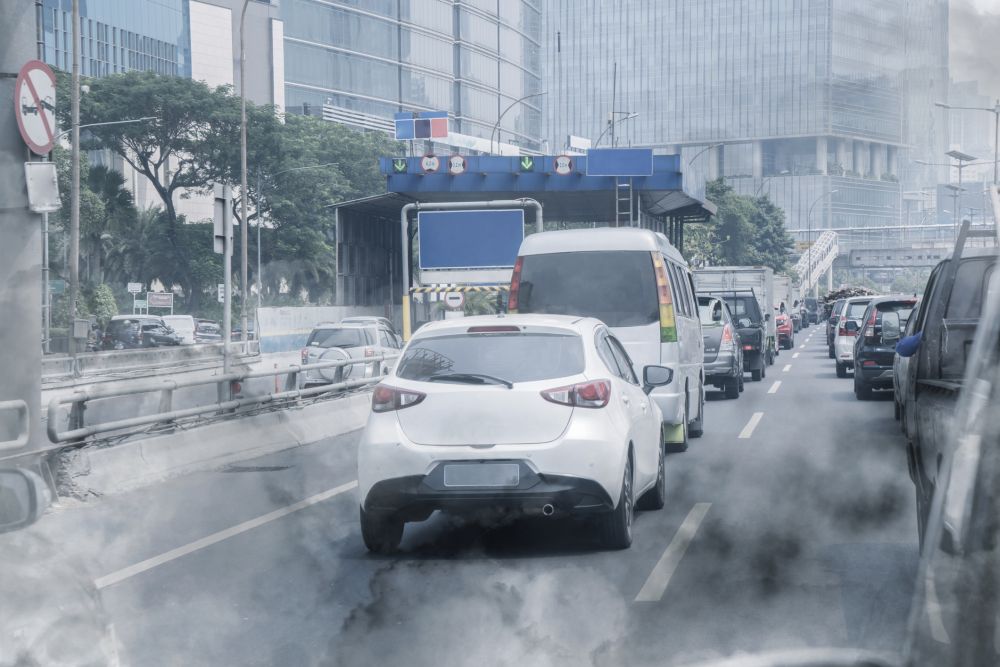

Exhaust gases irritate and directly damage our respiratory system
Heat waves and poor air quality often act as linked vessels as persistent high pressure creates a stagnant environment. With low winds and no precipitation, pollutants are not removed from the air and accumulate directly above the ground. With poor air quality, people can experience an acute deterioration of their health, accompanied by shortness of breath, a feeling that they cannot catch their breath, chest tightness, coughing from irritation or even bronchitis.
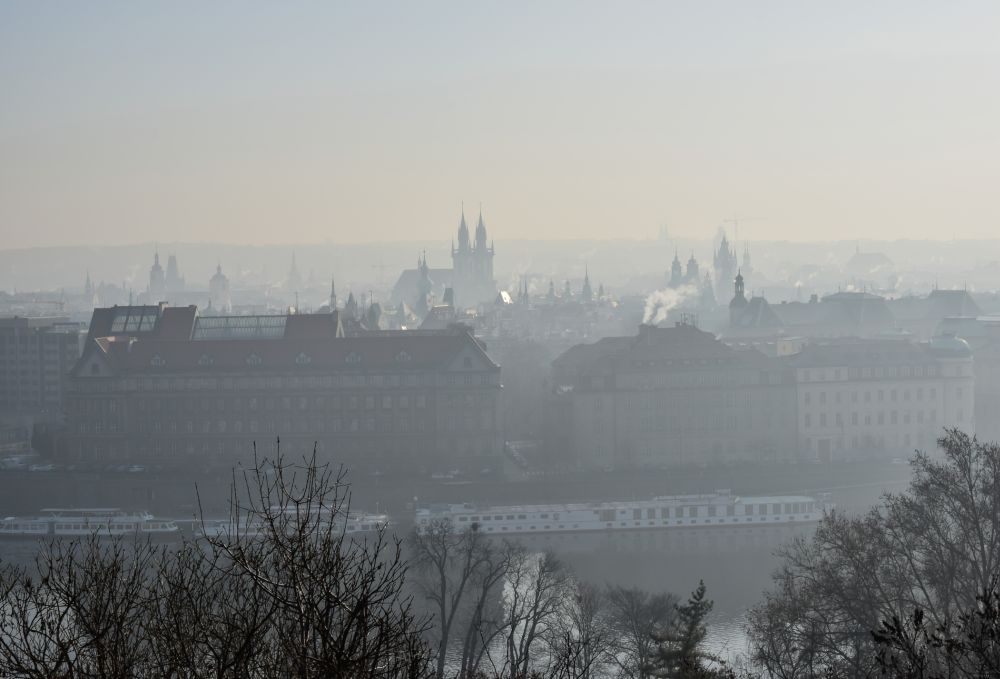

Smog situations in the summer are not pleasant, especially for asthmatics
Global warming and air pollution together represent one of the main public health problems in the world and in the Czech Republic. It is mainly felt by people who suffer from asthma. In our country alone, this disease afflicts roughly one in ten people and about 100 people die from it every year. We cannot yet effectively influence the quality of the outdoor air. However, most of us spend 90% of our time indoors, where dirt can be easily removed using high-quality air purifiers with a HEPA filter. This way you can significantly relieve your lungs and our body's defenses. And this is an essential help in times of increasingly frequent combinations of heat and polluted air.